Google reveals new information about the page title update and explains why it replaces some titles and not others.
The page title update rolled out last month, which replaces less than 20% of titles in SERPs with text Google considers more relevant to the query.
Since the initial rollout Google has further refined its system for generating page titles and now has additional guidance for everyone.
New Information About Google’s Page Title Update
Original Titles Used More Often
Webpages’ original titles will be used more frequently following the refinements to the page title update.
Original title elements are now used around 87% of the time, rather than around 80% when the update first rolled out.
Advertisement
Continue Reading Below
Why Doesn’t Google Always Use Original Titles?
Google will replace a page’s title in SERPs in cases when it does not describe a page as well as it could.
This has been going on since 2012, and Google’s recent update takes things a step further.
Here are some examples what Google’s page title update is designed to detect and adjust for:
Half-empty titles
Google’s new system is designed to detect half-empty titles, such as a title that displays just the site name, and adjust it by adding information found elsewhere on the page.
Obsolete titles
A page title can become obsolete when the same page is used year-after-year for recurring information, but the title stays the same.
Advertisement
Continue Reading Below
This type of adjustment could be as simple as updating the year in the title and keeping the rest the same.
Inaccurate titles
Sometimes titles do not accurately reflect what a page is about. Google gives the example of pages with dynamic content with a title element like: Giant stuffed animals, teddy bears, polar bears – Site Name.
This is an example of a static title for a page with content that dynamically changes. Some of those products might appear on the page and some might not.
Google may modify that title to more accurately reflect what’s on the page.
Micro-boilerplate titles
Micro-boilerplate titles refer to boilerplate title elements within a subset of pages within a site. Google’s system detects detects these titles and adjusts them.
“Consider an online discussion forum about television shows. It might have areas for different shows, and then for each show, it may have areas for threads for individual seasons.
The micro-boilerplate title elements appear on the season pages. The titles omit the season numbers, so it’s not clear which page is for what season.”
This is an example of a micro-boilerplate title:
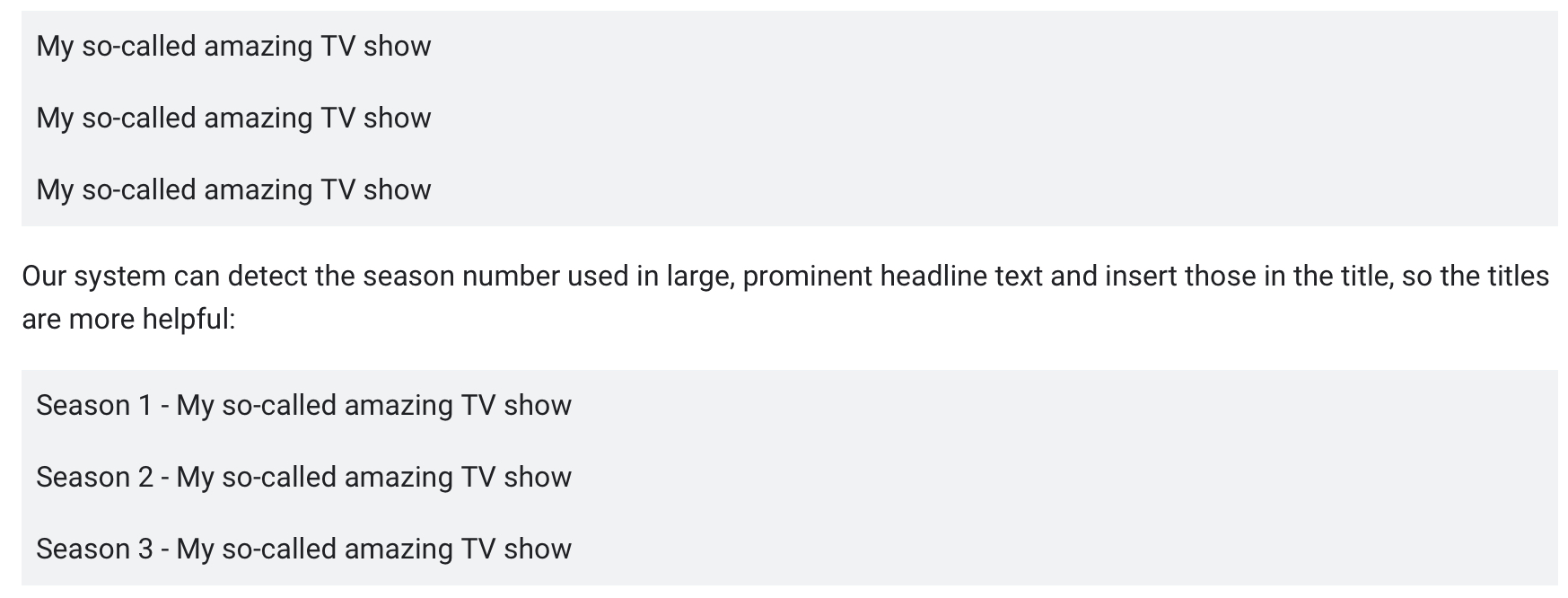 Screenshot from developers.google.com, September 2021.
Screenshot from developers.google.com, September 2021.Guidance From Google
Google’s guidance to site owners regarding the refinements to the page title update remains the same as when the update first launched.
Advertisement
Continue Reading Below
Google uses original titles most of the time, so focus more on writing great titles and less on the titles Google is replacing.
Lastly, Google adds:
“Beyond this, consider the examples in this post to understand if you might have similar patterns that could cause our systems to look beyond your title elements.
The changes we’ve made are largely designed to help compensate for issues that creators might not realize their titles are having. Making changes may help ensure your title element is again used. That’s really our preference, as well.”
Google may continue to refine its page title system even further after this latest update.
Advertisement
Continue Reading Below
Source: Google Search Central
Featured Image: Dennis Diatel / Shutterstock
 seolounge
seolounge